Flue Gas Desulphurisation (FGD), abbreviated as FGD in English, is currently the most widely used and the most direct, economical and effective method to reduce SO2 emissions, and is also the only large-scale application of the technology. At present, countries around the world pay great attention to flue gas desulphurisation and have developed dozens of effective desulphurisation technologies.
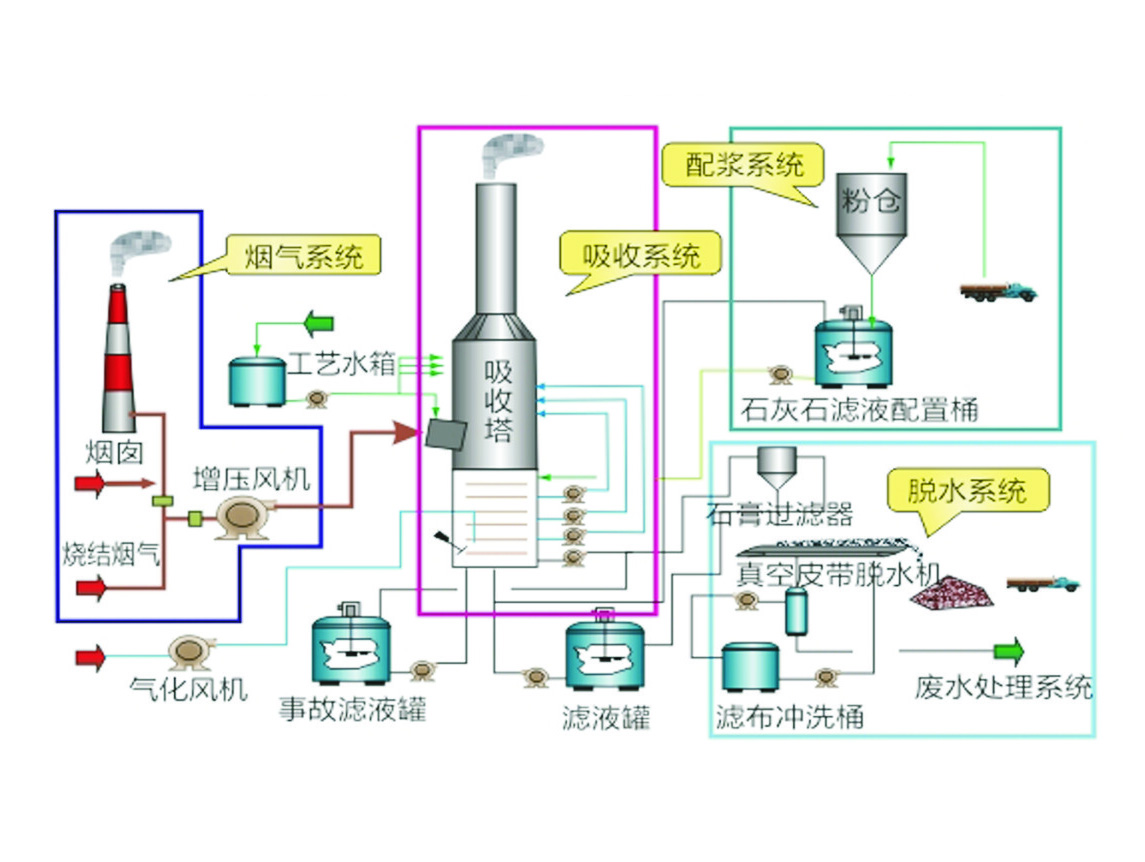
Flue gas desulphurisation (FGD) system mainly consists of the following sub-systems: limestone slurry preparation system, flue gas system, sulphur dioxide (SO2) absorption system (including slurry recycling and oxidation), gypsum dewatering system, process water system and wastewater treatment system.
Among all the methods, lime/limestone and gypsum wet flue gas desulphurisation technology is the most widely used, with high desulphurisation efficiency and good operational reliability. Lime/limestone and gypsum wet flue gas desulphurisation technology is one of the large-scale commercially applied desulphurisation methods in thermal power plants, and more than 90% of domestic and foreign thermal power plant desulphurisation technologies adopt lime/limestone and gypsum wet flue gas desulphurisation technology.
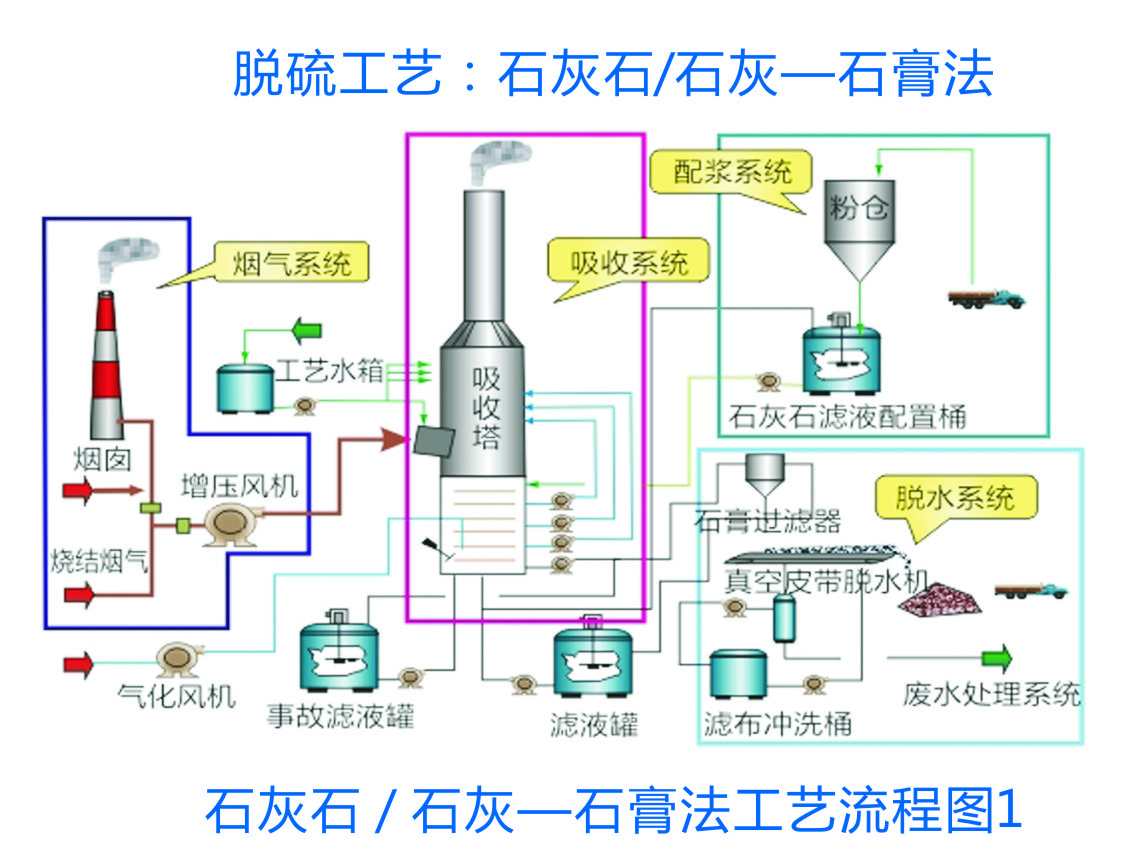
Figure shows a typical wet flue gas desulphurisation process diagram
◆Technical features:
1, suitable for combustion of high, medium and low sulfur any combustion boiler unit, SO2 treatment concentration ~ 25000mg/Nm³;
2, flue gas treatment capacity, cost-effective;
3, the absorption tower adopts spray air tower, system resistance is small;
4, desulfurization efficiency ≥ 95%;
5, calcium-sulfur ratio of ≤ 1.03;
6, desulfurization by-products of gypsum can be commercially utilized, moisture content of ≤ 15%;
7, the system utilization rate ≥ 90%.
Chemical reaction formula: SO2+H₂O+CaCO3--Ca(HSO3)+CO2(absorption)
Ca(HSO3)+O₂--CaSO4+H2SO4(oxidation)
CaCO3+H2SO4 --CaSO4+H₂O+CO3 (neutralisation)